Respiratory therapists are specialist and educators in cardiology and pulmonology. They focus on people who have trouble breathing from respiratory diseases like asthma and emphysema. They cater to patients of all ages, from infants born with undeveloped lungs to aged patients who have acquired lung diseases. They are also required for emergency treatments for patients who are suffering from heart attacks or shocks.
These respiratory therapists function under the guidance of a primary provider. These are the doctors or health specialists in operating rooms or out patient treatment centers.
Anyone who wants to be a respiratory therapist should take a 4 year course consisting of general science education subjects and professional subjects. During the last year, an internship program is necessary wherein students acquire training in a pulmonary laboratory, covering different hospital sections such as Pulmonary Diagnostics, General Respiratory Care, Pulmonary rehabilitation, Adult Intensive Care Unit, Neonatal and Pediatric Critical Care Unit, and Sleep Laboratory.
For those who do not have this course offered in schools in their location, there are also online courses available. There are many schools that offer respiratory therapy distance education. They are able to prepare their graduates with competencies in cognitive (knowledge), psychomotor (skills), and affective (behavior) learning domains of respiratory care practice. After graduating from this online course, the graduates are also eligible to take the National Board for Respiratory Care, and Advanced level credentialing exams. A full course is typically composed of 47 courses with a total of 113 credits.
Before enrolling for the course, you can check the course description as well as the offered subjects and credits on the website. Some sites even offer a net price calculator to assist students on determining the fees they need to pay for the entire year or full course. For further convenience, look for sites that offer a demo course for their classes. This allows you a sneak preview of how the classes are held and if that kind of system works for you. All you have to do is to go to their demo link, enter log in credentials, and you can view the demo course.
Distance learning has saved a lot of students time and money while earning their college degree. In the recent years, more and more courses have been made available online. Anyone who wants to earn their first degree or a secondary degree can finally do so without the hassles of commute, all with the help of technology.
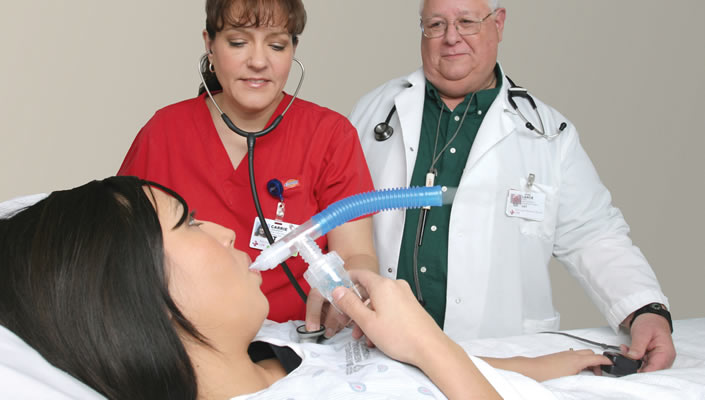
 Respiratory Therapists have been in high demand for many years now, and will be in the years to come. There is a great demand for health care professionals, and job stability is exceptional. There is a continued growth in biomedical technology which will ensure that the field will never get boring. And the opportunity to really help people and make a lasting and meaningful difference in the lives of others means you’ll get much more out of your career than just a paycheck.
Respiratory Therapists have been in high demand for many years now, and will be in the years to come. There is a great demand for health care professionals, and job stability is exceptional. There is a continued growth in biomedical technology which will ensure that the field will never get boring. And the opportunity to really help people and make a lasting and meaningful difference in the lives of others means you’ll get much more out of your career than just a paycheck.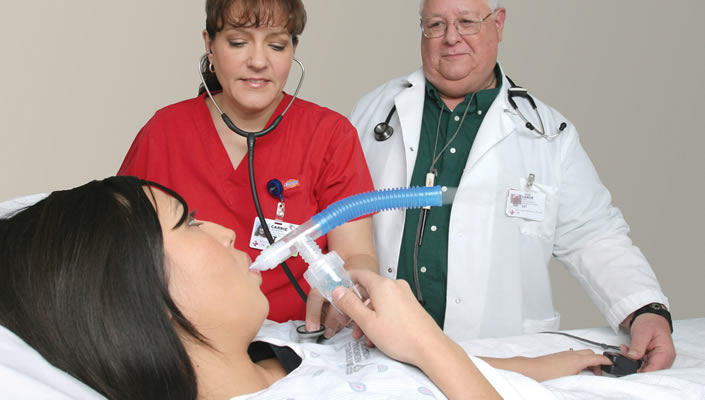
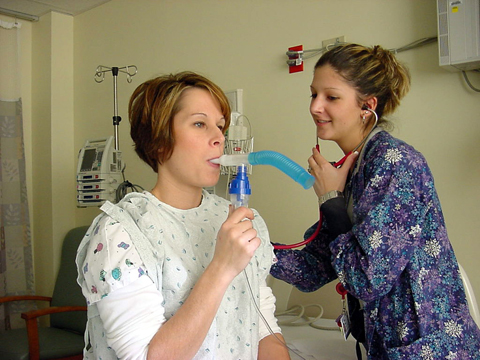 A new study finds that the respiratory therapists can help improve the detection rate of people with Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency. The year-long study aimed at detecting people with Alpha-1 referred for testing by RTs and the genotype distribution of referred people found to have Alpha-1. The study authors hypothesized that trained RTs could promote Alpha-1 testing, and in doing so, improve detection of those affected in the course of their routine practices.
A new study finds that the respiratory therapists can help improve the detection rate of people with Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency. The year-long study aimed at detecting people with Alpha-1 referred for testing by RTs and the genotype distribution of referred people found to have Alpha-1. The study authors hypothesized that trained RTs could promote Alpha-1 testing, and in doing so, improve detection of those affected in the course of their routine practices.